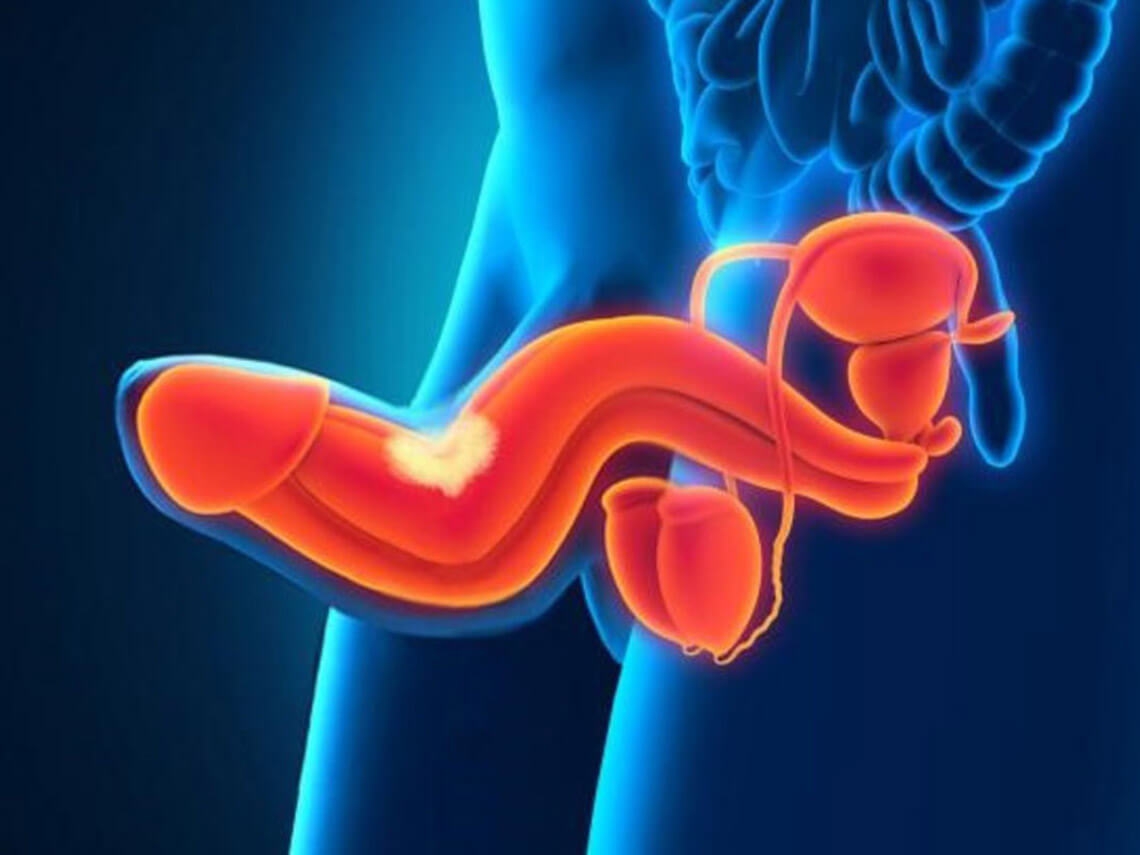
Fibroblastic induration of the penis (induration penis plastics), or Peyronie's disease, is the gradual compaction of areas of cavernous bodies with the formation of dense patches. The disease is observed mainly at the age of 40-60 years. The prevalence of the disease is 0.4-9%, more often in patients with diabetes and erectile dysfunction.
THE ETIOLOGY of the disease has not yet been definitively elucidated. One of the causes of this pathology is an abnormality of connective tissue, so it is attributed to collagenosis. Fibrostatic induration of the genital rod is often observed in patients with Dupuytren's contracture, scleroderma, Ledderhosis disease. Protein sheath damage (microvascular or traumatic), local inflammatory (long-term inflammatory response leads to remodulation of connective tissue into dense fibrous plaques), and autoimmune processes play a role in the etiopathogenesis of Peyronie's disease.
Risk factors
The most common comorbidities and risk factors are diabetes, hypertension, lipid metabolism disorders, ischemic cardiomyopathy, erectile dysfunction, smoking, and alcohol abuse. Patients with Peyronie's disease have an increased incidence of Dupuytren's contracture (with rates up to 9-39%), while Peyronie's disease occurs in 4% of patients with Dupuytren's contracture.
Pathogenesis
Peyronie's disease has 2 different stages of development. The first involves an acute inflammatory phase, which may be accompanied by a painful syndrome in a relaxed state or painful erections and is manifested by soft nodules/plaques and curvature of the penis. The second phase is fibrotic, with the formation of palpable hard plaques that can calcify, which also leads to stabilization of the disease without a further strengthening of the curve time, in 30-50% of patients the degree of curvature of the genital rod deteriorates, and in 50-67% it remains stable, with a frequency of spontaneous improvement of 3-13%. In 40% of patients in the early stages, there is pain, which is 90% passes within the first 12 months after the onset of the disease. In addition to physiological and functional disorders in the genitals, men are also under stress and have varying degrees of depression.
Clinical picture
The disease develops slowly. In the protein shell and cavernous bodies of the genital rod, in the membrane between the corpora cavernosa, often on its dorsal surface, there are dense painless or moderately painful, not associated with the surrounding tissues, oblong or annular plaques 1.5-2 cm long, 1.5-3-5 cm wide. Rarely are sealed in the form of a cord running along the back of the genital rod from head to root. Sometimes - along the urethra. Over time, due to the deposition of calcium salts in the compacted areas, the formation of bone tissue, they acquire a cartilaginous consistency. The urethra and its cavernous bodies are not involved in the pathological process. Nodes are never covered with ulcers, and their malignant degeneration does not occur. Patients complain of tightness in the genital rod, a curvature of the genital rod, and pain during erection, which sometimes makes it impossible to have intercourse.
DIAGNOSIS of fibroblastic induration of the genital rod is based on the curvature of the genital rod during erection. In the absence of an erection, the genital rod has the usual configuration. At its palpation cartilaginous consolidations come to light. During an erection, the genital ring is curved in the dorsal, lateral, medial, or other direction, depending on the location of the pathological process. Pay attention to the pain during erection, the length of the penis, the presence of stress.
It is necessary to assess the phase of disease activity, as it affects the type of conservative treatment and the time of surgery. The active phase is more likely in patients with a short duration of the disease, pain during erection, or changes in curvature in recent times. Absence of pain and stabilization of curvature for at least 3 months are widely accepted criteria for stabilization and referral of patients for surgical treatment if indicated.
It is important to measure the length of the penis during an erection, as this directly affects the tactics of treatment. It is also necessary to conduct an objective assessment of the degree of curvature of the genital rod (both in natural erection and in a vacuum-assisted erection, or after intracavernous injection of vasoactive drugs.
Ultrasound of the genital rod with Doppler vascular imaging is mandatory. Measure the size of the plaque and evaluate vascular parameters. MRI scans are also widely used.
Treatment of peyronie's disease.
Conservative treatment.
Patients with an early stage of the disease should be treated conservatively for Peyronie's disease.
Oral therapy includes:
- Vitamin E.
- Potassium paraaminobenzoate (Potaba)
- Tamoxifen
- Colchicine
- Acetyl esters of carnitine
- Pentoxifylline
- PDE inhibitors -5
Intraplastic therapy:
- Steroids
- Verapamil
- Clostridial collagenases
- Interferon
- Hyaluronic acid
Topical therapy:
- Verapamil
- Iontophoresis
- Shock wave therapy
- Gel H - 100
- Traction devices
Surgical treatment:
- Operation Nesbitt
- Application techniques
- Operations to lengthen the genital rod using grafts (autologous, cadaveric, synthetic)
- Implantation of penile prostheses